For a year or so, Brexit has been bad but ‘not apocalyptic’ to the UK economy

At the end of the first year of new trade between the UK and the EU, Brexit has become increasingly popular due to the lack of drama on the British border.
There have been a few remnants in the ports and a bit of a distraction in the flow of trade. But performance has been much lower than expected, even ahead of the turnaround trend next year, especially in food and agricultural products.
BrexitThe impact on the UK economy and public life appears to be dire but uncertain, according to economists.
He says the growth has already been affected by the new rules that came into effect on January 1 when the UK left the bloc. Over time, this could leave the country by about 4 percent worse than it would have been if the 2016 EU referendum went the other way, according to the Office for Budget Responsibility.
The economic crisis over Brexit has not been as serious as the big strike with life, but the biggest blow.
The exact cost is still unknown because the consequences were not immediate, financial experts say, and it is difficult to separate. effects of coronavirus infection.
One of the easiest ways to monitor Brexit, say economists, is to review the UK’s performance since the June 2016 referendum so far, in light of the uncertainty surrounding the Leave vote and what the country has done since then.
UK growth lags behind US and eurozone. Domestic sales in the UK were 3.9 per cent higher in the third quarter of 2021 compared to the second quarter of 2016. However, at the same time, the eurozone produced 6.2 per cent growth and US 10.6 per cent.
While the economic downturn in the UK is not being criticized, there could be a number of reasons other than Brexit.
Economists are concerned that differences in GDP and ONS estimates could temporarily upset the UK population. They are also affected by the growing number of non-Brexit-related growth, as well as the various Covid-19 epidemic experiences.
That is what could lead to the economic downturn, experts have tried more and more Brexit results, looking at trade results.
John Springford, deputy director of the Center for European Reform think-tank, compared how to use the UK’s business model based on the “doppelgänger UK” model, from the same countries.

The model showed that as of October, the most recent month in which data was available, UK exports to the UK were 15.7 per cent below the level that would have been expected if the UK had not abandoned EU alliance with a single market in January.
This review reflects the picture that, along with the departing EU citizens, Brexit “has made it difficult for Britain’s economic sector to adapt to the recession. [sectors after lockdown was lifted], ”Said Springford.
He also said that the uncertainty and falling prices after the referendum have caused the economy to lose about 4 to 5 percent of the national budget compared to what the UK voted to remain.
Julian Jessop, an independent economist and co-founder at the Institute of Economic Affairs think-tank, did not deny that Brexit has been economically weak, even though it supported the UK decision to leave the EU.
“There is no doubt that the things you can measure were negative,” he said.
Jessop added that low-income trade could lead to slower growth, but how trade activity could affect the economy “was highly uncertain”. However, the effects of trade cuts with the EU may be reduced over time, he said.
Although the controversy is still minor, Springford has not disputed the notion that the economic crisis may not be a clear indication. He also said that the “big question” for economists is that trade results could lead to GDP losses.
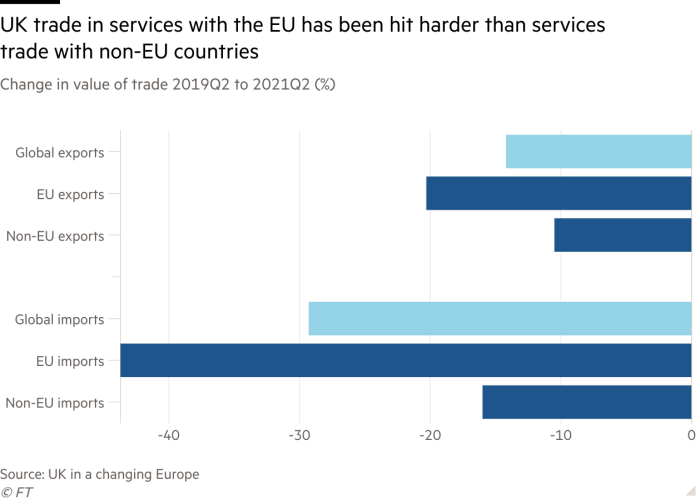
If commerce has deteriorated so far, Sarah Hall, a professor of economics at the University of Nottingham, thinks the impact of the UK service sector is a “resumption” rather than a major loss.
His research showed that UK exports in the second quarter of this year dropped by 14 percent two years ago, globally, reflecting the effects of Covid-19, particularly on tourism. However, exports to the EU fell by 30 percent, indicating a business and continental commitment.
Hall hopes the UK will try to reform its service sector over time to become a major global player, especially economically, and believes this has the potential to improve. While the consequences may be disastrous, he said, they will not be “apocalyptic”.
The shortage of truck drivers, farm workers and butchers has shown serious problems with the end of free movement. However, economists were surprised by the successful implementation of the new visa system to offset losses.
Jonathan Portes, a professor at King’s College London, said it was not surprising that the “collapse of the EU migration” because anyone wishing to come to the UK would have needed visas before 2021.
“We have seen professional visas work in the pre-epidemic period and, in particular, health and care visas have seen a success,” he said. “There has been a rapid reorganization of the NHS from EU staff to non-EU staff.”
“I didn’t think the Home Office could offer a new approach,” he added.
Economists emphasize that data comparisons have not yet been established.
New immigration laws enacted in the first half of 2022 have threatened to escalate tensions, says Springford, but HM Revenue & Customs’ commitment to prioritize business management in the management of the supply chain management system. management system management system management system management system management system management system management system management system management system management system management system management system management system management system management system management system management system
“HMRC will change the policy if the new rules create more problems at the border,” he said.
Kristalina Georgieva, IMF chief executive, briefed on the UK’s role in December. While acknowledging some of the obstacles that hinder the transition, he said “we are not in a position today, however, to know how this came about as a result of the epidemic and the role that Brexit could play in”.
The OECD warned in December that Britain’s relationship with the EU was important to its economy. “The growing trade ties with the European Union could also disrupt short-term economic growth,” it said.
As a result, the foreign policy is that Brexit has severely damaged the lives of the UK and every effort should be made to end its relations with the EU in order to reduce further damage.
Source link



